September 26, 2022 / Reading time: 5 minutes
Complete Guide to ARN (Amazon Resource Name) with Examples
- AWS ARN Formats
- Paths in ARN
- How to find ARN of AWS resources?
- How to find resource by ARN?
- ARN formats reference
ARN stands for Amazon Resource Name. It is a unique identifier for AWS resources. It is a string that contains information about the partition, service, region, account ID, and resource type. It is used to specify a resource unambiguously across all of AWS.
ARNs are used in AWS to uniquely identify resources. They are used in IAM policies, AWS CloudFormation templates, and API calls. They are also sometimes used in AWS CLI commands and AWS SDK calls.
AWS ARN Formats
ARN Formats are following a pattern that can be generalized into three main flavors:
arn:partition:service:region:account-id:resourcearn:partition:service:region:account-id:resourcetype/resource-idarn:partition:service:region:account-id:resourcetype:resource-id
Let's explain what each part of the ARN means:
arn
It is the ARN prefix. It is always the same and is used to identify that a string is an ARN.
partition
The partition that the resource is in. The standard AWS partition is aws. If you have resources in other partitions, the partition is aws-partitionname. For example, the partition for resources in the China (Beijing) Region is aws-cn.
service
The namespace of the AWS service that provides the resource. For example, an Amazon S3 bucket is in the s3 service namespace, and an Amazon EC2 instance is in the ec2 service namespace, and so on.
region
The AWS Region of the resource. An ARN may or may not include a region. If the ARN does not include a region, it is said to be a global resource. For example, IAM users are global resources.
account-id
12-digit ID of the AWS account that owns the resource, without hyphens.
resource
An identifier that uniquely identifies the resource. The format of this depends on the service. For example, an Amazon S3 bucket ARN includes the bucket name, such as arn:aws:s3:::my_corporate_bucket. An Amazon EC2 instance ARN includes the instance ID, such as arn:aws:ec2:us-east-1:123456789012:instance/i-1234567890abcdef0.
Let's take a look at each of these formats in detail. The first format is used for global services, such as IAM or S3.
Example:
arn:aws:iam::123456789012:root(AWS IAM User)arn:aws:s3:::my_corporate_bucket(AWS S3 Bucket)
The second format is used for regional services, such as Amazon EC2 where the resource type can be an instance, a security group, or a network interface and the part after the slash is the resource ID.
Example:
arn:aws:ec2:us-east-1:123456789012:instance/i-1234567890abcdef0(AWS EC2 Instance)arn:aws:ec2:us-east-1:123456789012:security-group/sg-1234567890abcdef0(AWS EC2 Security Group)
The third format is used for example for Lambda functions or Lambda Layers where the last part is the function version or layer version:
Example:
arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:my-function:2(AWS Lambda Function)arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:layer:my-layer:1(AWS Lambda Layer)
Paths in ARN
ARNs can also contain paths. Paths are used to identify specific resources inside a resource type. For example, an Amazon S3 object ARN includes the bucket name and the key of the object inside that bucket, such as arn:aws:s3:::my_corporate_bucket/exampleobject.png.
Wildcards in ARN Paths
ARNs can also contain wildcards. Wildcards are used to identify multiple resources inside a resource type. For example, an Amazon S3 object ARN includes the bucket name and the wildcard after the slash to identify all objects inside that bucket, such as arn:aws:s3:::my_corporate_bucket/*.
While this might seem to be helpful and easy to use, it is sometimes not recommended to use wildcards in ARN paths, especially when creating fine-grained IAM policies. It is against the principle of the least privilege. If it's possible, it is better to use specific resource names instead of wildcards.
How to find ARN of AWS resources?
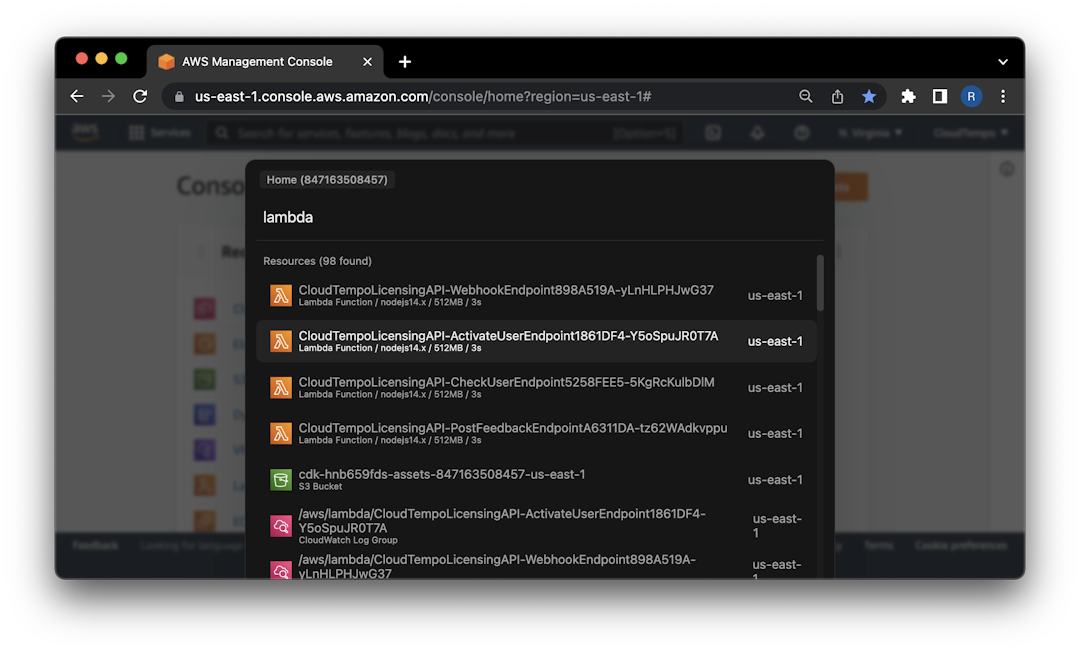
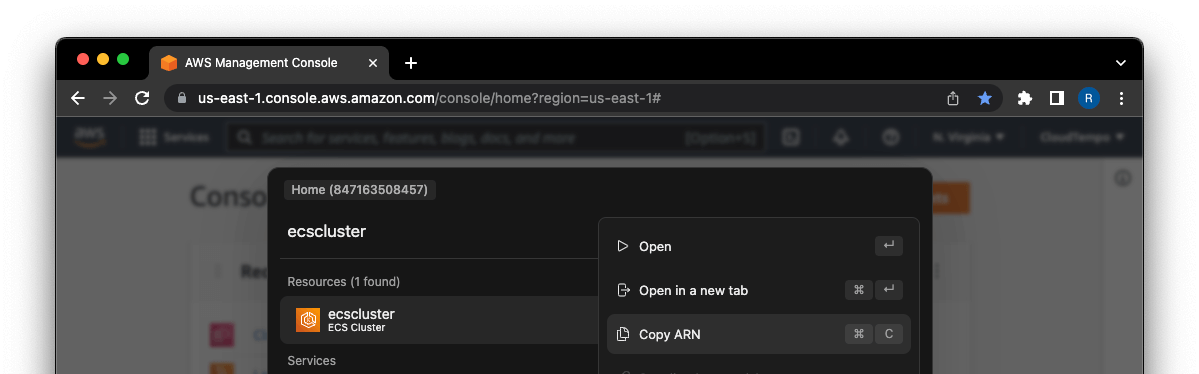
There are multiple ways to find ARN of AWS resources. The most obvious way is to use AWS Management Console. You can find ARN of any resource in the AWS Management Console by clicking on the resource and then clicking on the "Copy ARN" button. However, that is not always the best way to find ARN of AWS resources. Sometimes ARNs are not exposed or they're hard to find.
In such cases, you can use CloudTempo to find ARN of any AWS resource. Simply press ⌘ + K (on Mac) or CTRL + M (on Windows/Linux), type the name of the resource you want to find ARN of and press ⌘ + C or CTRL + C to copy the ARN to your clipboard.
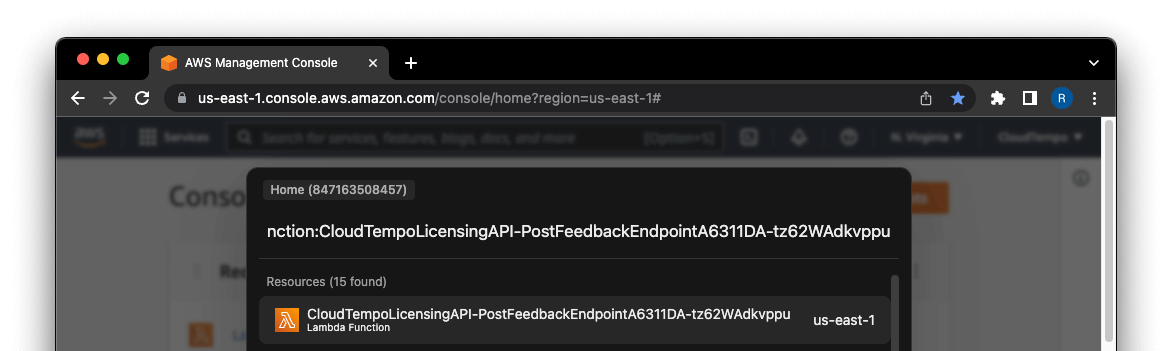
How to find resource by ARN?
Sometimes, you have an ARN but you don't know where the resource is in the AWS Console. CloudTempo helps you with that. Simply press ⌘ + K (on Mac) or CTRL + M (on Windows/Linux) and paste the ARN into the search bar. CloudTempo will open the resource in the AWS Console after pressing enter.
If you don't have CloudTempo, you can download it here.
ARN formats reference
Below you can find a list of ARN formats for some AWS services:
Amazon API Gateway
- API Stage:
arn:aws:apigateway:region::/restapis/api-id/stages/stage-name - Rest API:
arn:aws:apigateway:region::/restapis/api-id - Rest API Resource:
arn:aws:apigateway:region::/restapis/api-id/resources/resource-id - Rest API Resource Method:
arn:aws:apigateway:region::/restapis/api-id/resources/resource-id/methods/HTTP-VERB
AWS Lambda
- AWS Lambda Function:
arn:aws:lambda:region:account-id:function:function-name - Fully qualified AWS Lambda Function (with version):
arn:aws:lambda:region:account-id:function:function-name:version - AWS Lambda Layer with version:
arn:aws:lambda:region:account-id:layer:layer-name
Amazon S3
- Amazon S3 Bucket:
arn:aws:s3:::bucket-name - Amazon S3 Object:
arn:aws:s3:::bucket-name/object-key
Amazon EC2
- Amazon EC2 Instance:
arn:aws:ec2:region:account-id:instance/i-1234567890abcdef0 - Amazon EC2 Security Group:
arn:aws:ec2:region:account-id:security-group/sg-1234567890abcdef0 - Amazon EC2 Network Interface:
arn:aws:ec2:region:account-id:network-interface/eni-1234567890abcdef0
Amazon RDS
- Amazon RDS DB Instance:
arn:aws:rds:region:account-id:db:db-instance-id - Amazon RDS DB Cluster:
arn:aws:rds:region:account-id:cluster:db-cluster-id
Amazon DynamoDB
- Amazon DynamoDB Table:
arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name
AWS CloudFormation
- Amazon CloudFormation Stack:
arn:aws:cloudformation:region:account-id:stack/stack-name/stack-id - Amazon CloudFormation Stack Set:
arn:aws:cloudformation:region:account-id:stackset/stack-set-name:stack-set-id
AWS IAM
- AWS IAM User:
arn:aws:iam::account-id:user/user-name - AWS IAM Role:
arn:aws:iam::account-id:role/role-name - AWS IAM Group:
arn:aws:iam::account-id:group/group-name - AWS IAM Policy:
arn:aws:iam::account-id:policy/policy-name